For most of you, if you ever get a muscular injury from exercise or the wrong movement, you will immediately be recommended the RICE formula (rest, ice, compression, elevation). However, in recent years, scientists and doctors have started doubting whether ice is really helping more than it is hurting.
Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) has been used to treat and manage pain, injuries, and other maladies internally and externally in the body for thousands of years. Certain TCM therapies such as the use of chamomile, ginseng, garlic, and acupuncture have been growing in popularity among people in the West. However, people have also started looking to TCM to treat their muscle injuries as well.

They key to treating a muscle injury is inflammation
Inflammation is the first symptom you will receive, after the initial pain of course, when you injure a muscle. While inflammation might seem like something we want to prevent, it is actually necessary for the healing process. You see, when something threatens the body, whether it be an injury, wound, bacteria, or irritant, the body sends white blood cells to the area to try and prevent or treat the problem. In order for white blood cells to get to the affected area, your blood vessels become wider and, therefore, the area becomes hot and red.
What traditional Chinese medicine can help with is boosting your circulation so that those immune system cells can get to the right place faster and do their job better. Chinese medicinal herbs that promote blood circulation include:
- Winter Green Oil
- Papaya and Siberian Ginseng
- Gingko Pearl
- Radix Isatidis and Folium Perillae
- Motherwort

Treat muscle injuries with heat
The problem with ice is that it restricts the blood vessels in the injured area, which delays the body’s ability to naturally heal itself. Icing an injury provides temporary relief by reducing inflammation, but remember inflammation means the body is healing itself. We don’t want to impede that.
Instead, we should be using heat to bolster this natural immune system response. Heat speeds up cellular and metabolic activity, which leads to more optimized oxygen uptake, which boosts healing. Heat therapy can come in the form of Moxibustion (external therapy) and herbal remedies to promote blood circulation (internal therapy).
TCM directs the healing process
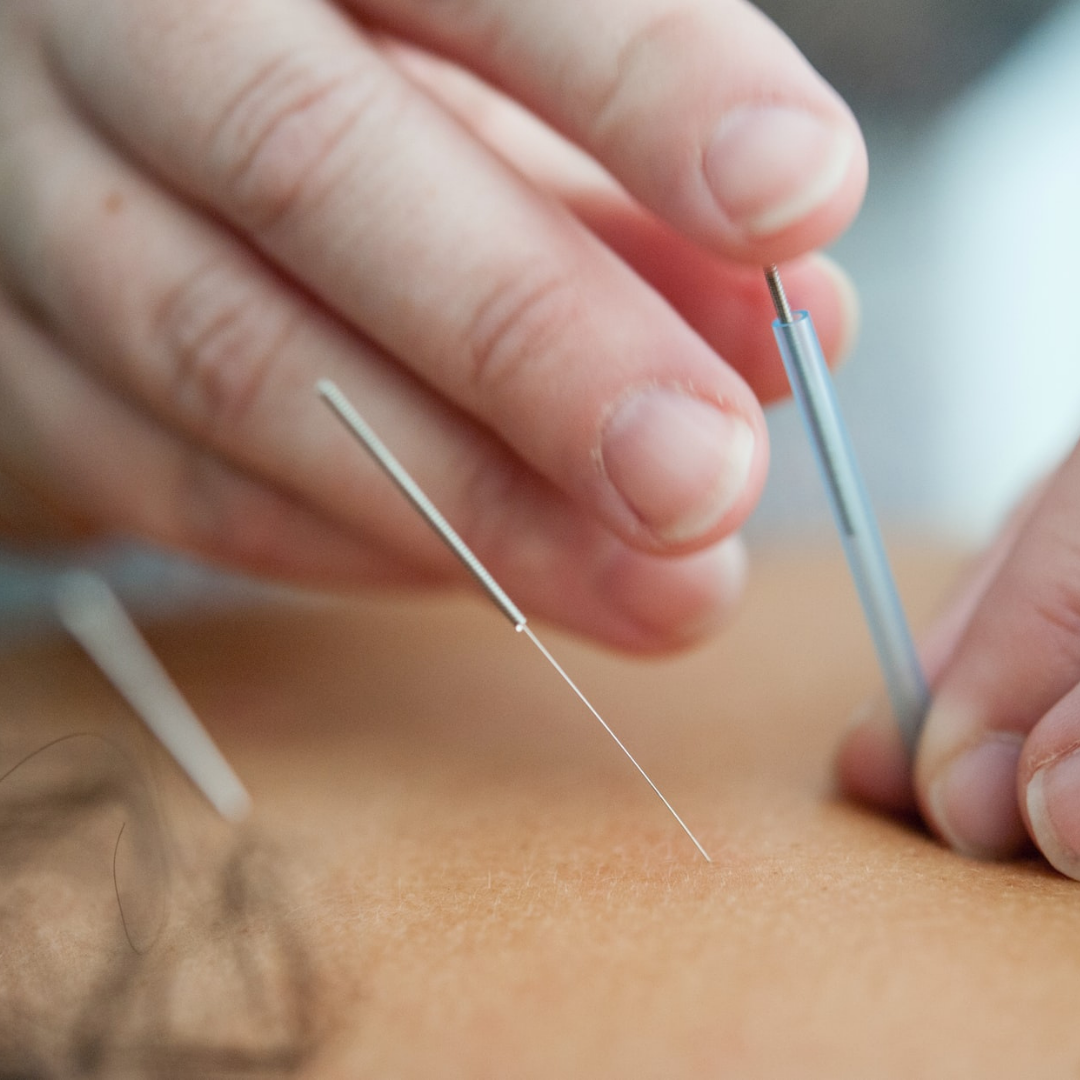
Acupuncture is an excellent therapy for muscle injuries. Acupuncture directs the body where to send its healing agents. Inserting needles in a certain area will create an immune response in that same area. Of course, immediately after a muscular injury, the area may be very sensitive. In this case, acupuncturists can go about it a couple different areas, depending on the injury. They can place their needles above and below the injury, increasing blood flow to the whole general area. They can also place needles in “mirrored” areas, such as the same muscle on the opposite side of the body. Once the muscles itself has progressed on its healing, needles can be placed there specifically to direct the healing process exactly where it needs to work.

Traditional Chinese medicine treats the body holistically
Let’s not forget that TCM is about balance. When the body is in balance, the immune system will naturally be better equipped to heal injuries and illnesses. While most Western medicine only treats the injured muscle, Chinese medicine focuses on treating the whole body, mind, and spirit. When all three are aligned, the body’s capacity to heal itself is vastly improved.
We are more than a bundle of muscles and blood vessels. TCM treats the body as a whole for holistic healing.
Consult a licensed physician when needed
Traditional Chinese medicine helps the body heal itself. However, there are some injuries that need specific orthopedic interventions. Always consult with licensed acupuncturists, certified herbalists, and physicians (to rule out more serious injuries) when putting together a treatment plan.



Leave a comment
All comments are moderated before being published.
This site is protected by hCaptcha and the hCaptcha Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.